diff options
Diffstat (limited to 'content/blog/2024-01-26-audit-dashboard.md')
| -rw-r--r-- | content/blog/2024-01-26-audit-dashboard.md | 203 |
1 files changed, 96 insertions, 107 deletions
diff --git a/content/blog/2024-01-26-audit-dashboard.md b/content/blog/2024-01-26-audit-dashboard.md index 5a40f51..d274eb1 100644 --- a/content/blog/2024-01-26-audit-dashboard.md +++ b/content/blog/2024-01-26-audit-dashboard.md @@ -5,9 +5,9 @@ description = "" draft = false +++ -Alteryx and Power BI are powerful tools that can help turn your -old-school audit trackers into interactive tools that provide useful -insights and potential action plans. +Alteryx and Power BI are powerful tools that can help turn your old-school audit +trackers into interactive tools that provide useful insights and potential +action plans. With these tools, we are going to build the following dashboard: @@ -18,59 +18,57 @@ With these tools, we are going to build the following dashboard: This project assumes the following: -- You have access to Alteryx Designer and Power BI Desktop. - - If you only have Power BI Desktop, you may need to perform some - analysis in Power BI instead of Alteryx. -- Your data is in a format that can be imported into Alteryx and/or - Power BI. -- You have a basic understanding of data types and visualization. +- You have access to Alteryx Designer and Power BI Desktop. + - If you only have Power BI Desktop, you may need to perform some analysis + in Power BI instead of Alteryx. +- Your data is in a format that can be imported into Alteryx and/or Power BI. +- You have a basic understanding of data types and visualization. # Alteryx: Data Preparation & Analysis ## Import Data -With Alteryx, importing data is easy with the use of the -`Input Data` tool. Simply drag this tool onto the canvas from -the `In/Out` tab in the Ribbon to create it as a node. +With Alteryx, importing data is easy with the use of the `Input Data` tool. +Simply drag this tool onto the canvas from the `In/Out` tab in the Ribbon to +create it as a node. -You can choose the File Format manually or simply connect to your -file/database and let Alteryx determine the format for you. For this -example, we will be importing an Excel file and changing the -`Start Data Import on Line` variable to `2`. +You can choose the File Format manually or simply connect to your file/database +and let Alteryx determine the format for you. For this example, we will be +importing an Excel file and changing the `Start Data Import on Line` variable to +`2`.  ## Transform Data -Next, let\'s replace null data and remove whitespace to clean up our -data. We can do this with the `Data Cleansing` tool in the -`Preparation` tab in the Ribbon. +Next, let's replace null data and remove whitespace to clean up our data. We +can do this with the `Data Cleansing` tool in the `Preparation` tab in the +Ribbon. Ensure that the following options are enabled: -- Replace Nulls - - Replace with Blanks (String Fields) - - Replace with 0 (Numeric Fields) -- Remove Unwanted Characters - - Leading and Trailing Whitespace +- Replace Nulls + - Replace with Blanks (String Fields) + - Replace with 0 (Numeric Fields) +- Remove Unwanted Characters + - Leading and Trailing Whitespace 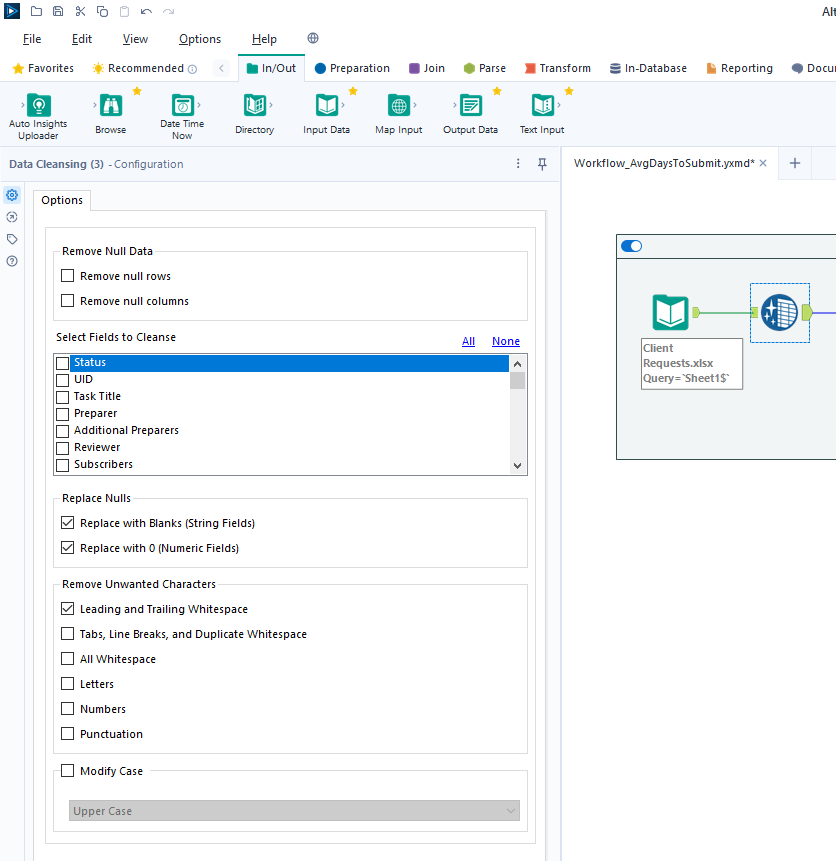 -For our next step, we will transform the date fields from strings to -datetime format. Add a `Datetime` tool for each field you -want to transform - in the example below, I am using the tool twice for -the \"Started On\" and \"Submitted On\" fields. +For our next step, we will transform the date fields from strings to datetime +format. Add a `Datetime` tool for each field you want to transform - in the +example below, I am using the tool twice for the "Started On" and "Submitted +On" fields. 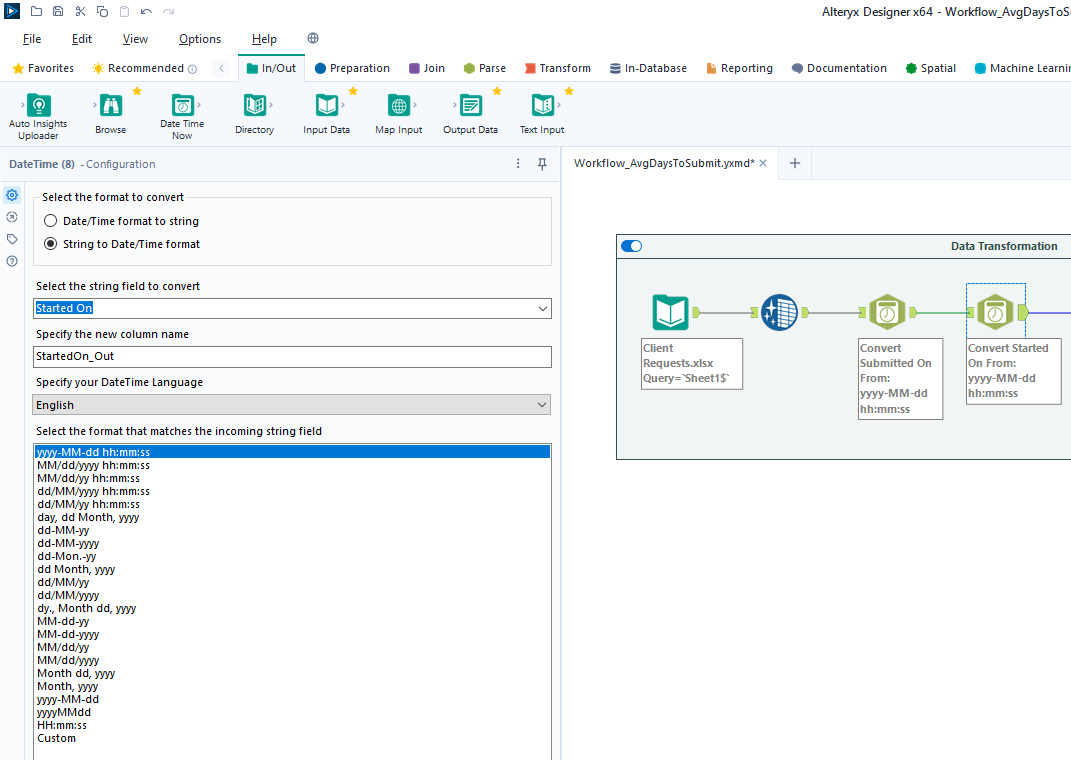 -Now that the dates are in the correct format, let\'s perform a -calculation based on those fields. Start by adding a `Filter` -tool, naming a new Output Column, and pasting the formula below into it -(the two fields used in this formula must match the output of the -`Datetime` tools above): +Now that the dates are in the correct format, let's perform a calculation based +on those fields. Start by adding a `Filter` tool, naming a new Output Column, +and pasting the formula below into it (the two fields used in this formula must +match the output of the `Datetime` tools above): ``` txt DateTimeDiff([SubmittedOn_Out],[StartedOn_Out], "days") @@ -81,8 +79,8 @@ Analysis](https://img.cleberg.net/blog/20240126-audit-dashboard/alteryx_analysis ## Export Data -Finalize the process by exporting the transformed data set to a new -file, for use in the following visualization step. +Finalize the process by exporting the transformed data set to a new file, for +use in the following visualization step. 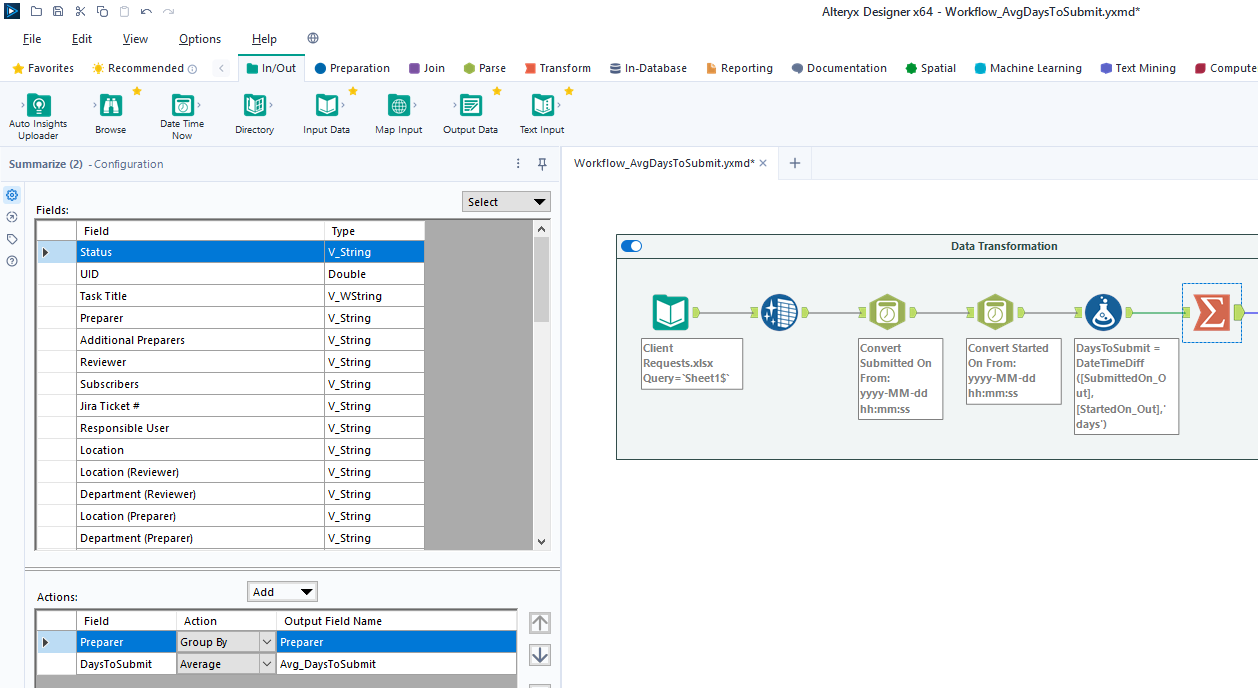 @@ -91,17 +89,15 @@ Export](https://img.cleberg.net/blog/20240126-audit-dashboard/alteryx_export.png ## Import Data -To start, open the Power BI Desktop application. Upon first use, Power -BI will ask if you want to open an existing dashboard or import new -data. +To start, open the Power BI Desktop application. Upon first use, Power BI will +ask if you want to open an existing dashboard or import new data. -As we are creating our first dashboard, let\'s import our data. In my -example below, I\'m importing data from the \"Tracker\" sheet of the -Excel file I\'m using for this project. +As we are creating our first dashboard, let's import our data. In my example +below, I'm importing data from the "Tracker" sheet of the Excel file I'm +using for this project. -During this process, I also imported the export from the Alteryx -workflow above. Therefore, we have two different files available for use -in our dashboard. +During this process, I also imported the export from the Alteryx workflow above. +Therefore, we have two different files available for use in our dashboard.  @@ -111,78 +107,71 @@ Import](https://img.cleberg.net/blog/20240126-audit-dashboard/powerbi_import.png ## Add Visuals -To create the dashboard below, you will need to follow the list -instructions below and format as needed: +To create the dashboard below, you will need to follow the list instructions +below and format as needed: 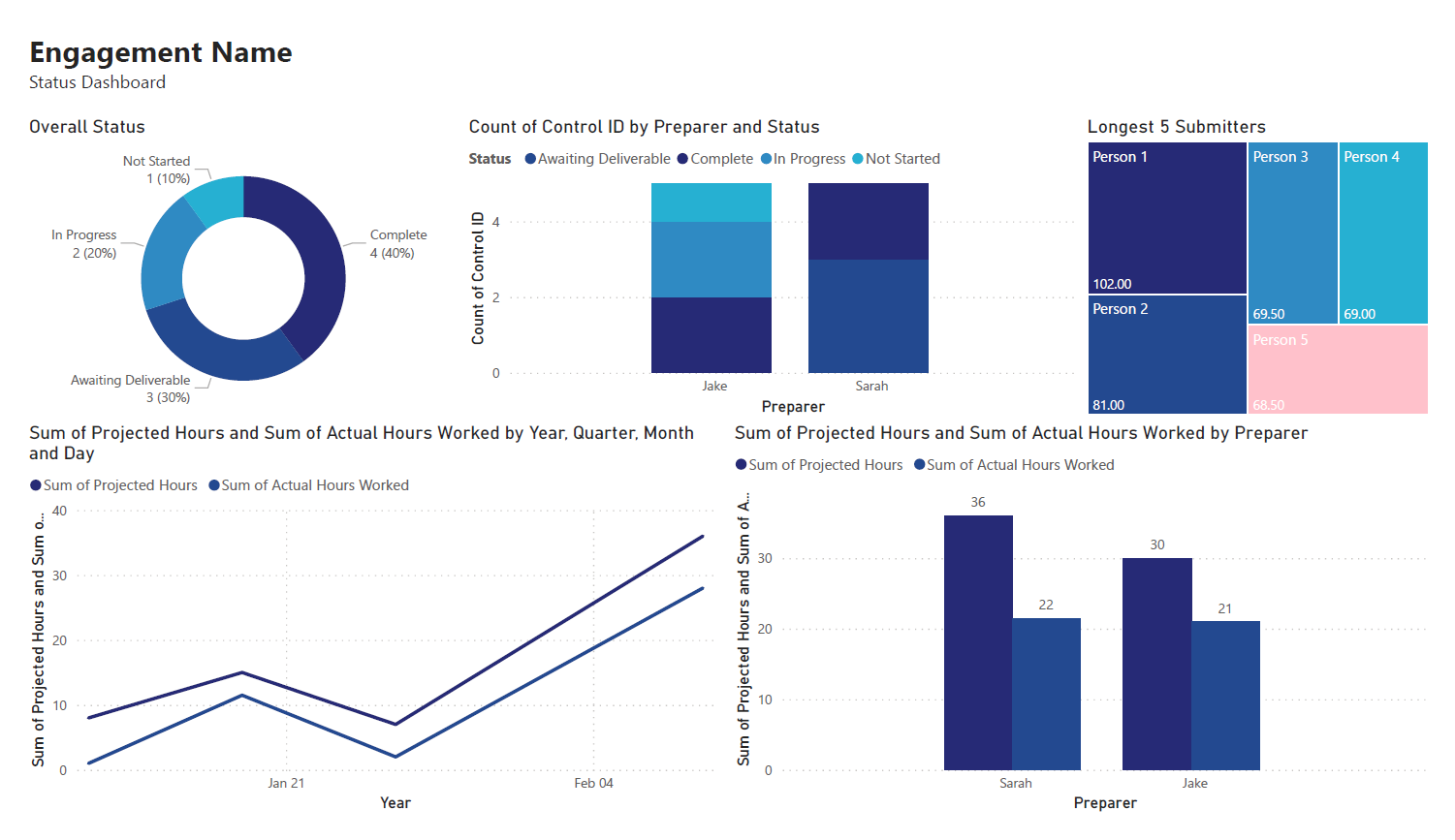 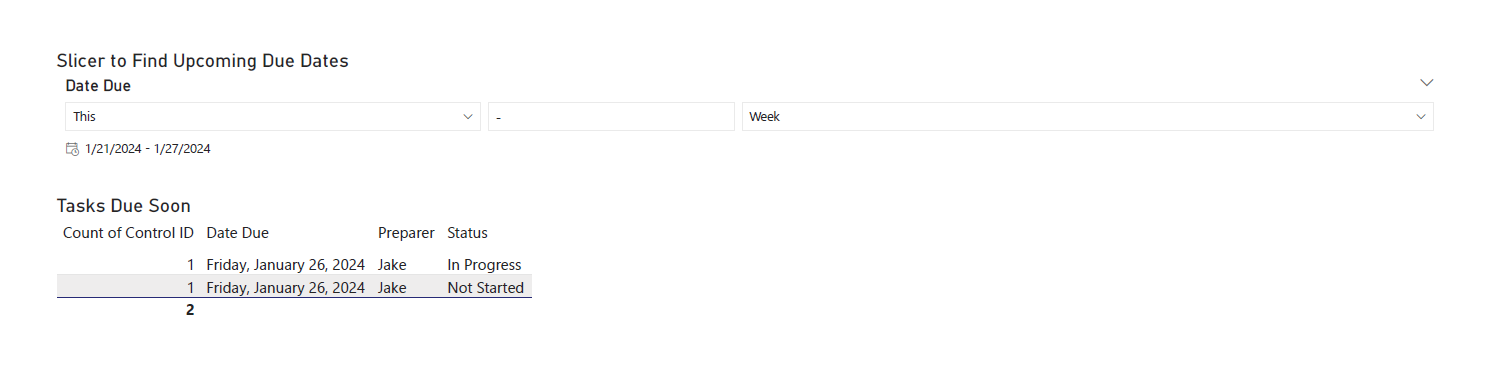 Instructions to create the visuals above: -- `Text Box`: Explain the name and purpose of the - dashboard. You can also add images and logos at the top of the - dashboard. -- `Donut Chart`: Overall status of the project. - - `Legend`: Status - - `Values`: Count of Status -- `Stacked Column Chart`: Task count by assignee. - - `X-axis`: Preparer - - `Y-axis`: Count of Control ID - - `Legend`: Status -- `Treemap`: Top N client submitters by average days to - submit. - - `Details`: Preparer - - `Values`: Sum of Avg~DaysToSubmit~ -- `Line Chart`: Projected vs. actual hours over time. -- `Clustered Bar Chart`: Projected vs. actual hours per - person. -- `Slicer & Table` - Upcoming due dates. - - `Slicer`: - - `Values`: Date Due - - `Table`: - - `Columns`: Count of Control ID, Date Due, - Preparer, Status +- `Text Box`: Explain the name and purpose of the dashboard. You can also add + images and logos at the top of the dashboard. +- `Donut Chart`: Overall status of the project. + - `Legend`: Status + - `Values`: Count of Status +- `Stacked Column Chart`: Task count by assignee. + - `X-axis`: Preparer + - `Y-axis`: Count of Control ID + - `Legend`: Status +- `Treemap`: Top N client submitters by average days to submit. + - `Details`: Preparer + - `Values`: Sum of Avg~DaysToSubmit~ +- `Line Chart`: Projected vs. actual hours over time. +- `Clustered Bar Chart`: Projected vs. actual hours per person. +- `Slicer & Table` - Upcoming due dates. + - `Slicer`: + - `Values`: Date Due + - `Table`: + - `Columns`: Count of Control ID, Date Due, Preparer, Status ## Format the Dashboard -You can choose a theme in the View tab of the Ribbon. You can even -browse for custom JSON files that define themes, such as ones found -online or custom ones created by your organization. - -For each visual, you can click the `Format` button in the -`Visualizations` side pane and explore the options. You can -custom options such as: - -- Visual - - Legend - - Colors - - Data labels - - Category labels -- General - - Properties - - Title - - Effects - - Header icons - - Tooltips - - Alt text - -You can always look online for inspiration when trying to decide how -best to organize and style your dashboard. +You can choose a theme in the View tab of the Ribbon. You can even browse for +custom JSON files that define themes, such as ones found online or custom ones +created by your organization. + +For each visual, you can click the `Format` button in the `Visualizations` side +pane and explore the options. You can custom options such as: + +- Visual + - Legend + - Colors + - Data labels + - Category labels +- General + - Properties + - Title + - Effects + - Header icons + - Tooltips + - Alt text + +You can always look online for inspiration when trying to decide how best to +organize and style your dashboard. # Sharing the Results -Generally, you have a few different options for sharing your dashboards -with others: - -1. Export the dashboard as a PDF in the file menu of Power BI. This - will export all tabs and visuals as they are set when the export - button is pressed. You will lose all interactivity with this option. -2. Send the full Power BI file to those you wish to share the - dashboard. This will retain all settings and interactivity. However, - you will also need to send the source files if they need to refresh - the dashboard and you will need to re-send the files if you make - updates. -3. Store the dashboard in a synced location, such as a shared drive or - Microsoft Teams. Depending on how a user configures their local - Windows paths, the data source paths may not be compatible for all - users with such a setup. +Generally, you have a few different options for sharing your dashboards with +others: + +1. Export the dashboard as a PDF in the file menu of Power BI. This will export + all tabs and visuals as they are set when the export button is pressed. You + will lose all interactivity with this option. +2. Send the full Power BI file to those you wish to share the dashboard. This + will retain all settings and interactivity. However, you will also need to + send the source files if they need to refresh the dashboard and you will need + to re-send the files if you make updates. +3. Store the dashboard in a synced location, such as a shared drive or Microsoft + Teams. Depending on how a user configures their local Windows paths, the data + source paths may not be compatible for all users with such a setup. |
